Types of gemstones
Colored Gemstones
Gemstones have fascinated cultures across the ages with their beauty, symbolism, and legendary powers. Beyond the “big three” — sapphires, emeralds, and rubies — there are many other captivating stones such as amethyst, garnet, and turquoise. While generally more abundant and accessible, these gems still offer striking beauty and rich variety. Traditionally, the distinction between these and the big three has been based on factors like rarity, brilliance, and color intensity, all of which influence a gem’s appeal and market value. That said, some of these so-called “semi-precious” stones can command prices equal to or even exceeding those of the traditional top-tier gems.

Amethyst
Color: Colorless to various shades (yellow, pink, blue, etc.)
Characteristics: Known for its exceptional hardness (10 on the Mohs scale) and brilliance. Diamonds are valued for their clarity, cut, and color

Garnet
Color: Red, but also found in green (tsavorite), orange (spessartite), and other colors
Characteristics: Includes several varieties such as almandine, pyrope, and tsavorite.

Citrine
Color: Yellow to golden brown
Characteristics: A variety of quartz, often used as a more affordable alternative to yellow diamonds.

Topaz
Color: Ranges from clear to various shades of blue, yellow, and pink
Characteristics: Known for its clarity and vibrant colors, with blue topaz being particularly popular.

Peridot
Color: Olive green to yellow-green
Characteristics: Known for its bright green color and is one of the few gemstones that occur in one color.

Aquamarine
Color: Light to medium blue, sometimes with a greenish tint
Characteristics: A variety of beryl, valued for its clear, pale blue color.

Tourmaline
Color: Comes in a wide range of colors including pink, green, and blue
Characteristics: Includes various types like pink tourmaline, green (chrome) tourmaline, and the rare Paraíba tourmaline.

Moonstone
Color: Colorless to white, with an iridescent play-of-color
Characteristics: Known for its adularescence (a soft glow that seems to move across the surface).
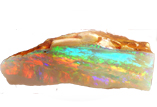
Opal
Color: Various colors, often with a play-of-color effect (e.g., black opal, fire opal)
Characteristics: Unique for its ability to display multiple colors and patterns.
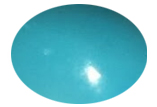
Turquoise
Color: Blue to green
Characteristics: An opaque gem known for its distinctive color and use in various cultures.

Lapis Lazuli
Color: Deep blue with gold flecks (pyrite) and white veins (calcite)
Characteristics: Valued for its rich blue color and historical significance.

Jasper
Color: Found in a variety of colors and patterns
Characteristics: An opaque, often multicolored or patterned variety of chalcedony.

Onyx
Color: Typically black, but also available in various colors and patterns
Characteristics: Known for its smooth, glossy finish and consistent color.

Chrysoprase
Color: Bright green
Characteristics: A variety of chalcedony with a vivid green color due to nickel content.

Labradorite
Color: Gray to dark brown with iridescent flashes of color (known as labradorescence)
Characteristics: Valued for its unique optical effect.

Sardonyx
Color: Alternating bands of sard (reddish-brown) and onyx (black or white)
Characteristics: Known for its banded appearance and use in cameo carvings.

Malachite
Color: Bright green with distinctive banding
Characteristics: Often used in decorative pieces and jewelry.

Spinal
Color: Available in a wide range of colors including red, pink, blue, and black
Characteristics: Known for its brilliance and is often mistaken for ruby or sapphire.
While there are hundreds of semi-precious gemstones in the world, we’ve curated this list to focus on the 18 types that are most popular and widely used in jewelry and decorative pieces. These selections include stones that offer the best combination of beauty, availability, and market demand. By concentrating on these key gemstones, we ensure that our customers have access to the most versatile and sought-after options, ranging from timeless classics to trendy favorites.